Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) related tyramine reaction MAOIs reduce first pass metabolism of tyramine, allowing greater concentrations to reach the sy · When ingested as food, tyramine doses ofWe propose an MAOI diet that has a solid scientific and clinical basis and that is, above all, practical MAO RIMAs Phenelzine Isocarboxazid Tranylcypromine MAOI interactions Tyramine structure The MAOI diet refined The clinicial pharmacology of MAOIs Refs and further reading HOME HedWeb Nootropics erythroxylumcocacom Future Opioids BLTC

Pdf Tyramine Potentiation During Treatment With Mao Inhibitors Brofaromine And Moclobemide Vs Irreversible Inhibitors
Tyramine maoi interaction
Tyramine maoi interaction-If you take an MAOI and you eat hightyramine foods, tyramine can quickly reach dangerous levels This can cause a serious spike in blood pressure and require emergency treatment Avoid consuming foods that are high in tyramine if you take an MAOI You may need to continue following a lowtyramine diet for a few weeks after you stop the medication · If you're taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), it's important to avoid foods high in tyramine, as the interaction could raise blood pressure to dangerously high levels Tyramine and MAOIs Tyramine is a monoamine compound found naturally in some foods and also produced in foods when they are fermented, aged or spoiled, notes Vanderbilt University
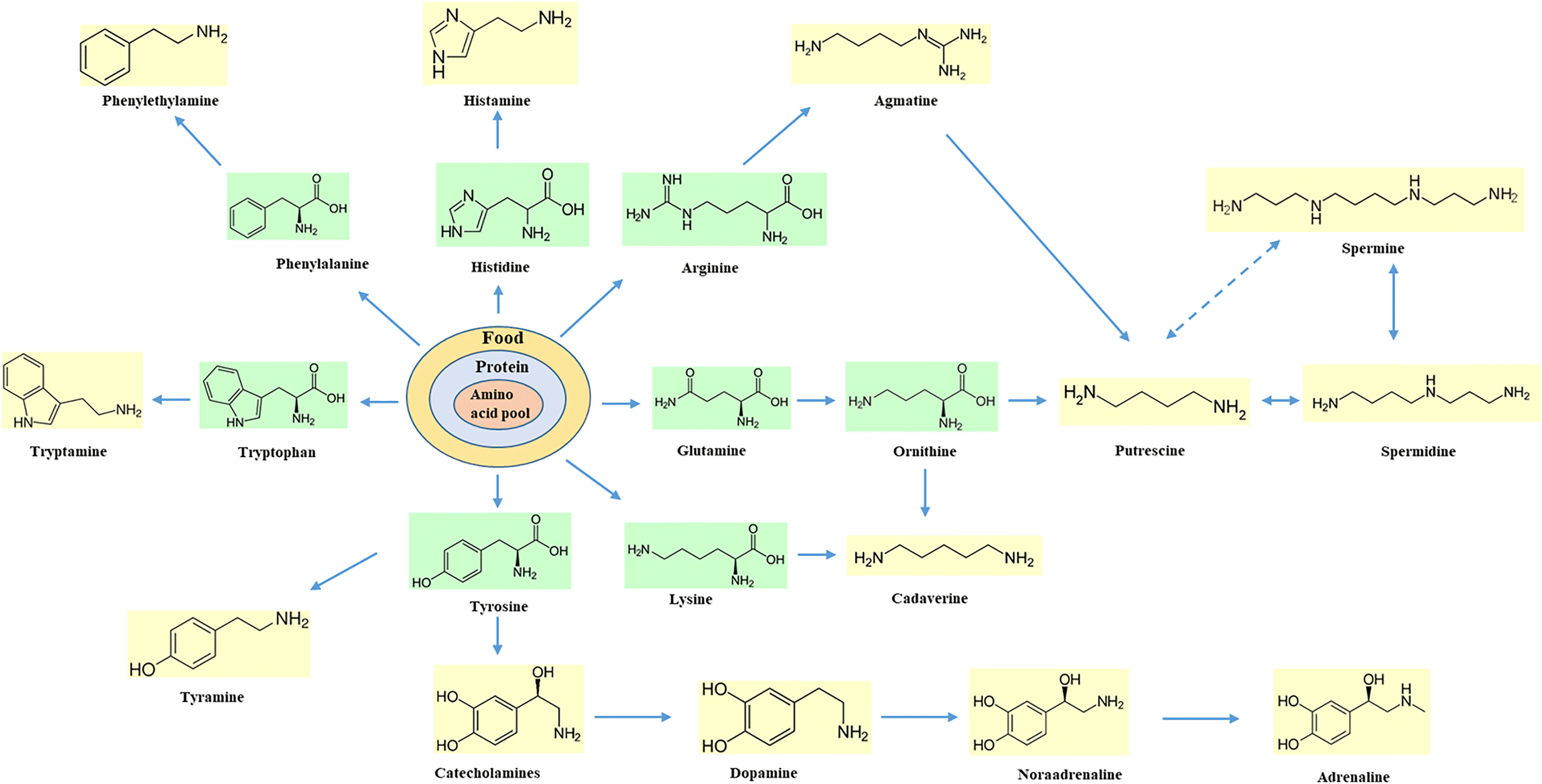


Chapter 1 Biogenic Amines Formation Toxicity Regulations In Food Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039
MAOIs have no clinically relevant pharmacokineticinteractions The only significant pharmacodynamicinteraction, other than the pressor response to tyramine ('cheese reaction'), is serotonin toxicity (ST)— aka serotonin syndrome · So while you are taking MAOIs for depression, Dr Edlund explains, your body is already working harder to process naturally occurring tyramine Any tyramine that comes from your diet is "extra," and can easily accumulate in your body and overload the systemTyramine, also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent Notably, it is unable to cross the bloodbrain barrier, resulting in only nonpsychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion A hypertensive crisis can result, however, from ingestion of tyramine
· so degree of tyramine interaction varies with type of MAO A or B inhibitor regarding judged potency of inhibition with IC50 values, from an interesting paper on MAOI flavonoids which i've posted in Passifloras thread here it seems that for potency, values of 15 microM is 'very good', 630 is still 'pretty good', and as we reach 100 microM were're getting into · Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are types of antidepressants used to treat depression MAOIs are an older class of antidepressants that are not used as much because of drug and food interactions MAOIs also are used to treat Parkinson's disease SSRIs are also used to treat anxietySelective inhibition of MAOA allows for tyramine to be metabolised via MAOB Agents that act on serotonin if taken with another serotoninenhancing agent may result in a potentially fatal interaction called serotonin syndrome or with irreversible and unselective inhibitors (such as
Low Tyramine Diet What is tyramine?1919 · Food and beverage interactions MAOIs can cause dangerous interactions with certain foods and beverages You'll need to avoid foods containing high levels of tyramine ― an amino acid that regulates blood pressure ― such as aged cheeses, sauerkraut, cured meats, draft beer and fermented soy products (for example, soy sauce, miso and tofu)Diet and Hypertensive Crisis See also Dr Ken Gillman Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI), Tyramine and Drug Interactions (Abbreviated) Tyramine is a pressor agent (ie increases blood pressure) and is normally metabolized by MAOA in the gut and the liver



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library
MAOIs interact with tyramine, a naturally occurring substance found in certain foods In some individuals this interaction can cause a sudden increase in blood pressure, leading to pounding of the heart, severe headache and tightness of the chestTyramine causes hypertensive crises after MAO inhibition aka the "cheese effect" or "cheese crisis" Using a MAO inhibitor (MAOI), the intake of approximately 10 to 25 mg of tyramine is required for a severe reaction compared to 6 to 10 mg for a mild reaction Tyramine rich food should also be avoided by people prone to headache and migraineInteraction of MAO inhibitors and dietary tyramine a new experimental model in the conscious rat J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 1994 Dec;32 (4) doi / (94)



Pdf Tyramine Potentiation During Treatment With Mao Inhibitors Brofaromine And Moclobemide Vs Irreversible Inhibitors
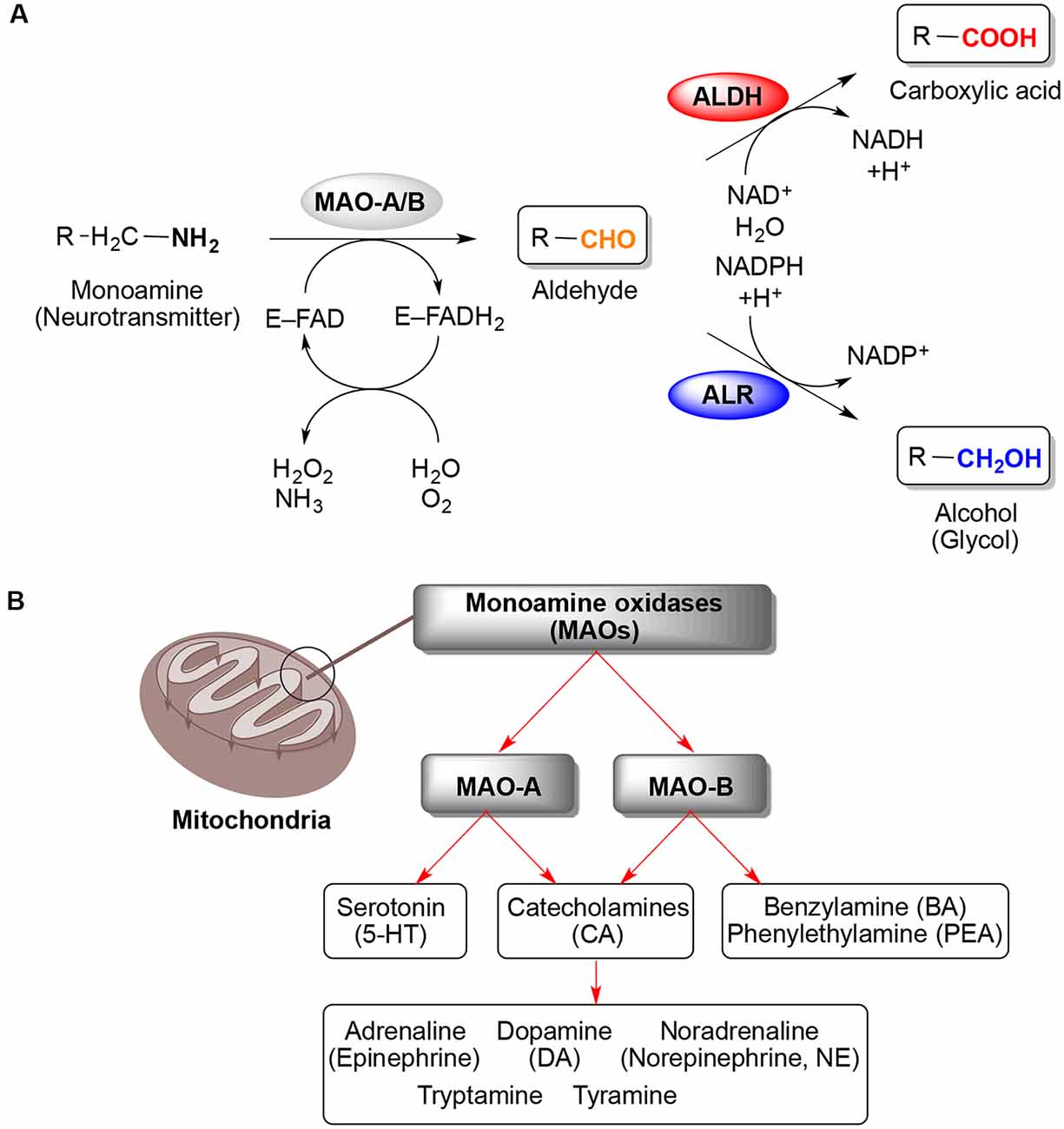


Frontiers Monoamine Oxidases Maos As Privileged Molecular Targets In Neuroscience Research Literature Analysis Molecular Neuroscience
You won't be able to have some foods and drinks while you are taking an MAOI because there is a potential for a serious interaction Tyramine is a compound that affects your blood pressure It's regulated and broken down by the MAO enzyme MAOIs restrict the MAO enzyme to reduce symptoms of depression and anxietyDopamine and the dietary (exogenous) amines, tyramine and tryptamine, are substrates for both forms of MAO 47 In the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and the liver, MAO catabolizes a number of dietary pressor amines (such as dopamine, tyramine, tryptamine, and phenylethylamine) 48 For this reason, consumption of certain foods (that contain high levels of dietary amines) while on an MAOITyramine is an amino acid which is found in various foods see Erowid Note, and is an indirect sympathomimetic that can cause a hypertensive reaction in patients receiving MAOI therapyMonoamine oxidase is found in the gastrointestinal tract and inactivates tyramine;



Tyramine And Health
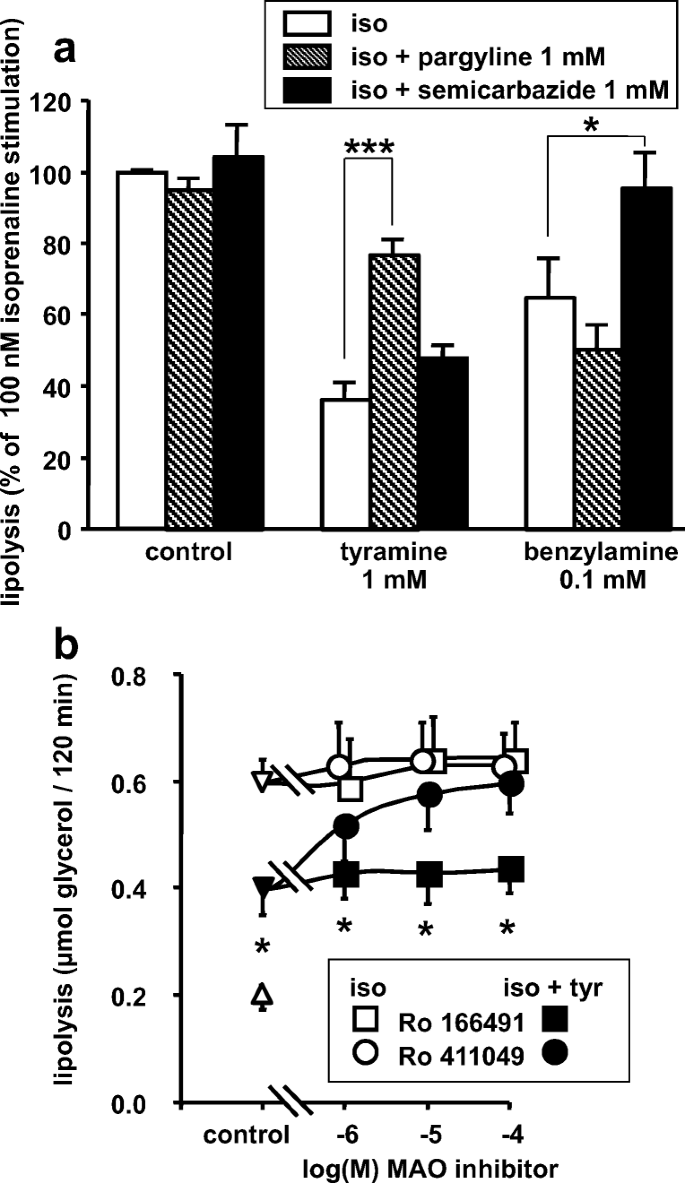


Mechanisms Of The Antilipolytic Response Of Human Adipocytes To Tyramine A Trace Amine Present In Food Springerlink
0406 · A dangerous interaction can occur when a patient on MAOIs eats foods rich in the amino acid tyramine Normally, the monoamine oxidase enzyme keeps tyramine at safe levels in the body But when the enzyme is inhibited by MAOIs, tyramine metabolism is inhibited, and the amino acid may build up to excessive levelsSummary The history of monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (MAOIs) is full of controversy due to their interactions with certain foodstuffs and other drugs The most feared interaction of MAOIs is the interaction with tyramine, a compound contained in a number of foods and beverages This interaction may lead to hypertensive crises the socalled 'cheese reaction'Tyramine is a monoamine and acts indirectly to release catecholamines Tyramine is typically metabolized by monoamine oxidase in the gut, a process that MAOIs interfere with Tyramine is found in preserved meat, fish, cheese, alcohol, and proteinrich foods which are particularly likely to contain bacteria that convert amino acids into monoamines like tyramine



Dietary Restrictions Drug Interactions With Maoi Psychiatrist Com



Pdf Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors A Review Concerning Dietary Tyramine And Drug Interactions
MAOI Interactions with Other Drugs While aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol) (plain), ibuprofen (Motrin) or antibiotics are safe when combined with an MAOI, you should check with your doctor before taking any other medicine1907 · Food interactions MAOIs can interact with foods that contain tyramine and cause a dangerous increase in blood pressure You'll need to avoid certain foods while you're using this type of medication Your healthcare provider will provide a list of foods to avoid while you're using any type of MAOI to treat depression or another condition · Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs, MAOI) is a class of antidepressants They are infrequently prescribed because of concerns about interactions with particular foods and several drug interactions Side effects, drug interactions, storage, dosage, and pregnancy safety information should be reviewed prior to taking any medication



This Is Specially For Italians Because None Tells Them About Tyramine If You Suffer From Headache Or Migraine This Is Headache Diet Maoi Diet Migraine Diet
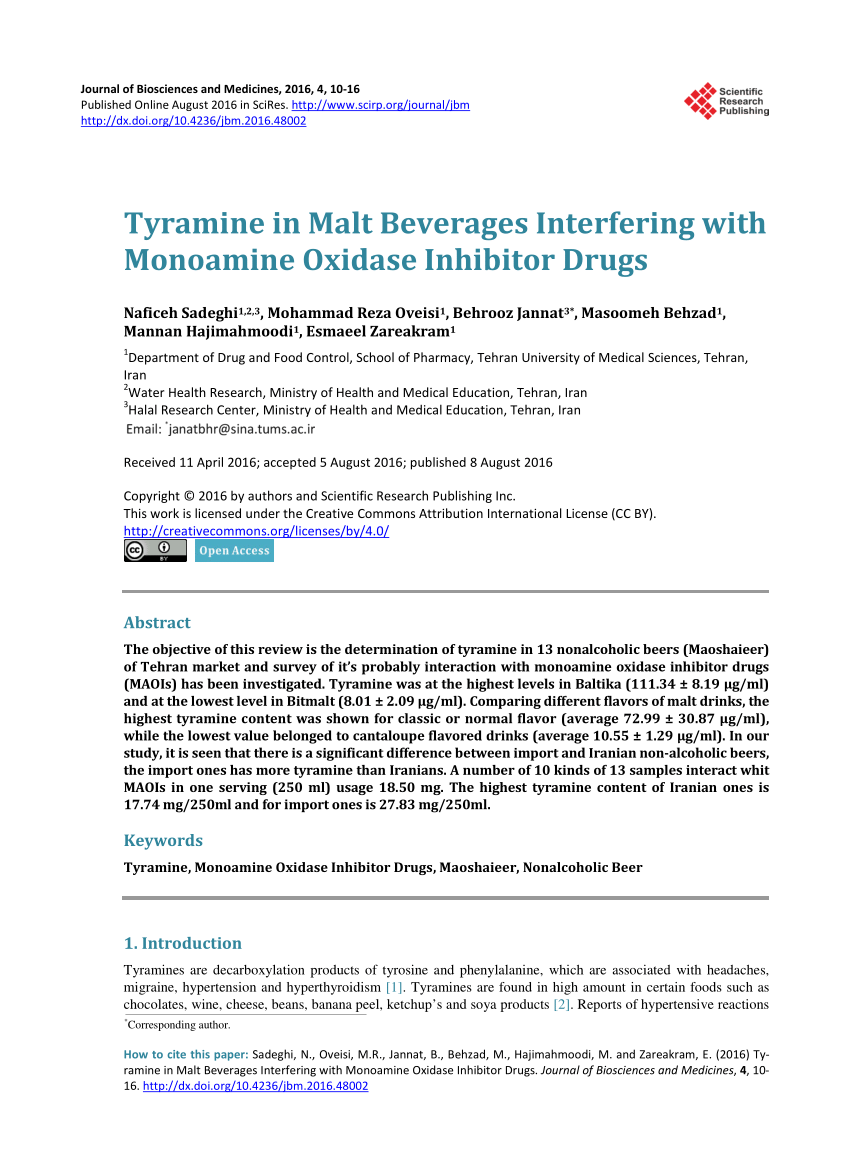


Pdf Tyramine In Malt Beverages Interfering With Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Drugs
When drugs prevent the catabolism of exogenous tyramine, this amino acid is absorbed and displaces2312 · Mainly freshly prepared food, and eliminates foods that are high in tyramine, including soy sauce, yeast and meat extracts, fermented foods and mature cheeses However, many foods once thought to be dangerous for patients on MAOIs are now allowed A tyramine content of less than 6mg per serving is generally considered safe• Tyramine is a naturally occurring substance that is present in certain foods • Some foods contain greater amounts of tyramine than others instance,For foods that have been aged, matured, fermented, pickled, smoked or that are past the "best before" or "use by" date



The Relationship Between Tyramine Levels And Inflammation In Metabolic Syndrome
/GettyImages-746275147-5b0b3813fa6bcc0037205902.jpg)


Dietary Precautions While Taking Maois
Reports of hypertensive reactions from monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) began to proliferate in the early 1960s Asatoor did extensive research and found that the combination of an MAOI and a food containing tyramine resulted in the hypertensive interaction ("the cheese reaction") Because of the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage and death, · An acute attack of hypertension that can occur in a person taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) drug who eats cheese, caused by an interaction of the MAOI with tyramine, formed in ripe cheese when bacteria provide an enzyme that reacts with the amino acid tyrosine in the cheese Other foods and drinks that produce the same effect include pickledTyramine Foods List, Tyramine Free Diet, Tyramine Reaction, Low Tyramine, Tyramine Food Chart, Tyramine Rich Foods List, Maoi Diet, Tyramine Foods to Avoid, Migraine Diet Food List, High Tyramine Foods, Migraine Food Triggers List, Histamine Food List, Low Tyramine Headache Diet, Amine Food List, Tyramine Containing Foods List, Lysine Foods List, Serotonin Foods List, All Foods with Tyramine



Tyramine Wikipedia
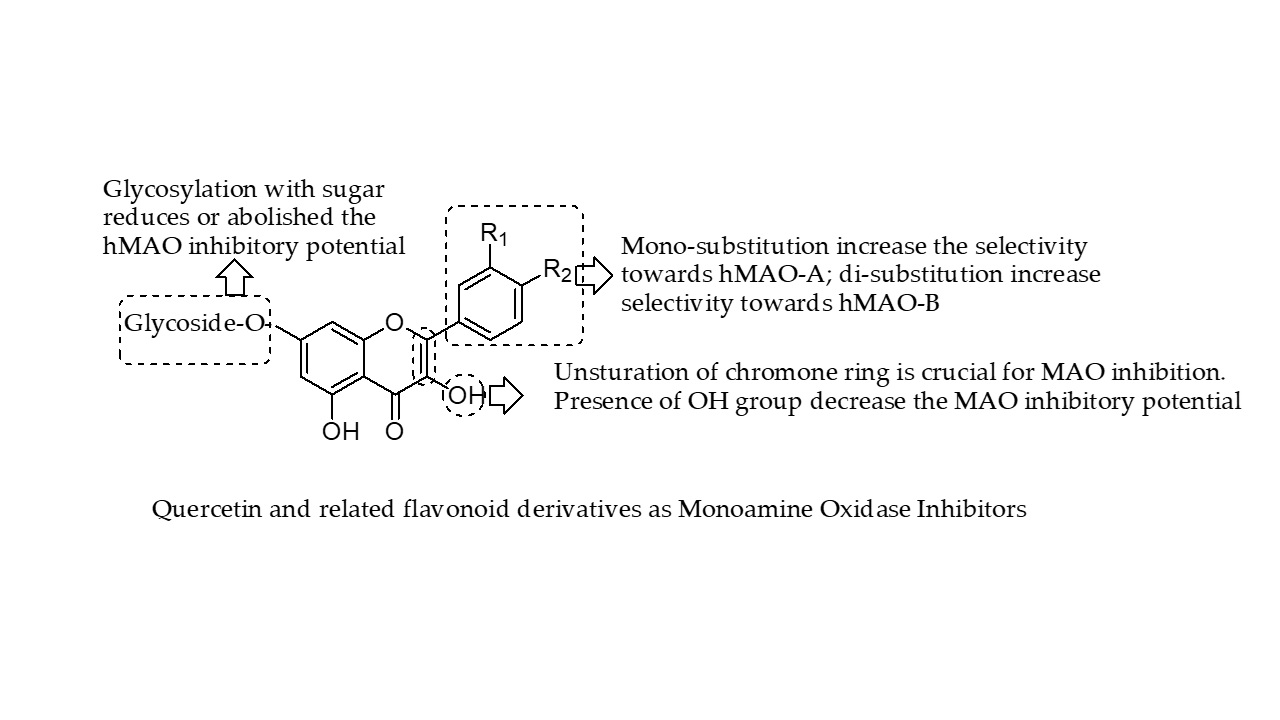


Molecules Free Full Text Quercetin And Related Chromenone Derivatives As Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Targeting Neurological And Mental Disorders Html
0217 · Drug Interactions There are no significant pharmacokinetic interactions that involve MAOIs, Reference Gillman 8 which is more than can be said for most other "new" drugs The main serious interaction between MAOIs and other therapeutic drugs is the pharmacodynamic interaction of serotonin toxicity (ST), which is caused only by the coingestion of serotonin · We now understand that the only serious interaction between MAOIs and TCAs is caused by excessive elevations of serotonin Such great elevations of serotonin (5HT) can only be produced if MAOIs are combined with therapeutic doses ofThere are two types of dangerous reactions that can occur with an MAOI and certain other drugs The first is Serotonin Toxicity or Syndrome (ST or SS) This is the result of using a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) and an MAOI concurrently



Tyramine And Mao Inhibitors Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Tyramine And Maoi Page 1 Line 17qq Com
· It was referred to as an MAOI "B" medication, and the older products became known as MAOI "A" medications Eutonyl, Eutron, and Marplan are no longer marketed Regarding MAOI therapy, one set of precautions is paramount MAOIs block the body's ability to metabolize tyramine, carrying a high potential for drug and food interactions0119 · Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI) are Best known to be powerful antidepressants They are effective therapeutic agents for panic disorder and social phobia MAOIs are tried when other antidepressants don't work, due to side effects MAOIs can cause dangerous interactions with foods and beverages that contain Tyramine See table belowCheddar Cheese and Moclobemide;
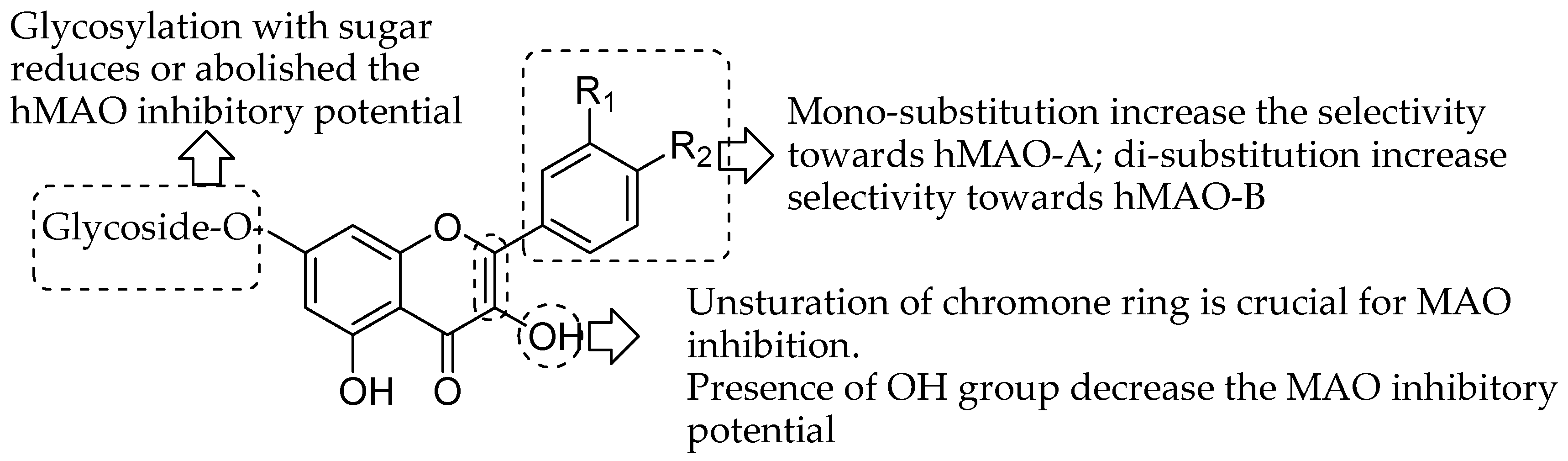


Molecules Free Full Text Quercetin And Related Chromenone Derivatives As Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Targeting Neurological And Mental Disorders Html
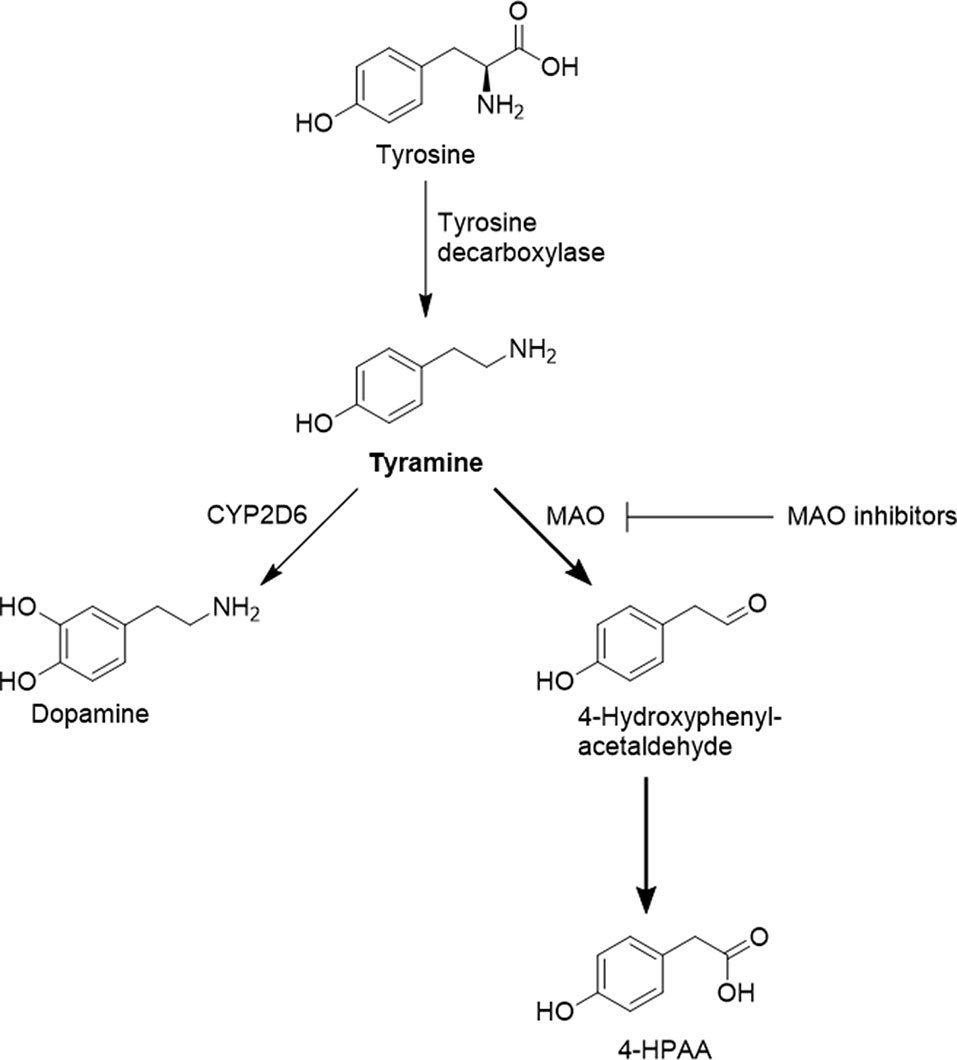


Frontiers Highly Variable Pharmacokinetics Of Tyramine In Humans And Polymorphisms In Oct1 Cyp2d6 And Mao A Pharmacology
2702 · This shields the body from foods with high levels of tyramine, which have to potential to cause adrenergic hyperstimulation This protective property of MAOA is critical to the understanding of · In conclusion, if the dietary tyramine response in rats treated with MAO inhibitors is predictive of the clinical situation (oral tyramine absorbed from a meal), our model is adequate for studying the interaction between MAOI's and tyramine The authors thank Mrs Anne Le Kim, Aline Perisse, and Miss Pascale Briand for expert technical assistanceMore Thoughts on MAOI Interactions Cheddar Cheese and Moclobemide Anonymous (1996) We had this argument about tyramine and selective MAOIA's some time ago, and the data shows that tyramine is NOT a *large* problem with selective / reversible MAOIAs "No rise in bloodpressure was noted in 6 healthy subjects whore received cheddar cheese with tyramine



Meal Ideas And Menus Avoiding High Tyramine Foods Made Easy Kathrynne Holden Ms Rd Pdf Free Download



Cheese Reaction Mechanism Mao Inhibitors Tyramine Drug Interactions Pharmacology Made Easy Youtube
A monoamine oxidase inhibitor, or MAOI, is a type of antidepressant drug In addition to depression, MAOIs also treat Bipolar & Panic disordersTyramineInduced Hypertension Crisis Tyramine is a compound found in many foods This compound has an effect on blood pressure and is regulated by the MAO enzyme When the MAO enzyme is inhibited (for instance, when you take an MAOI), tyramine can reach dangerously high levels, resulting in critically high blood pressureMyth MAOIs have many dangerous interactions with other drugs Yet there are only two interactions just SRIs and releasers (ISAs) The potentially risky interactions with MAOIs are 1 Serotonin syndrome, caused by (S)SRIs MAOIs 2 Blood pressure elevation, caused by tyramine in food, or by the other releasers like ephedrine & pseudoephedrine
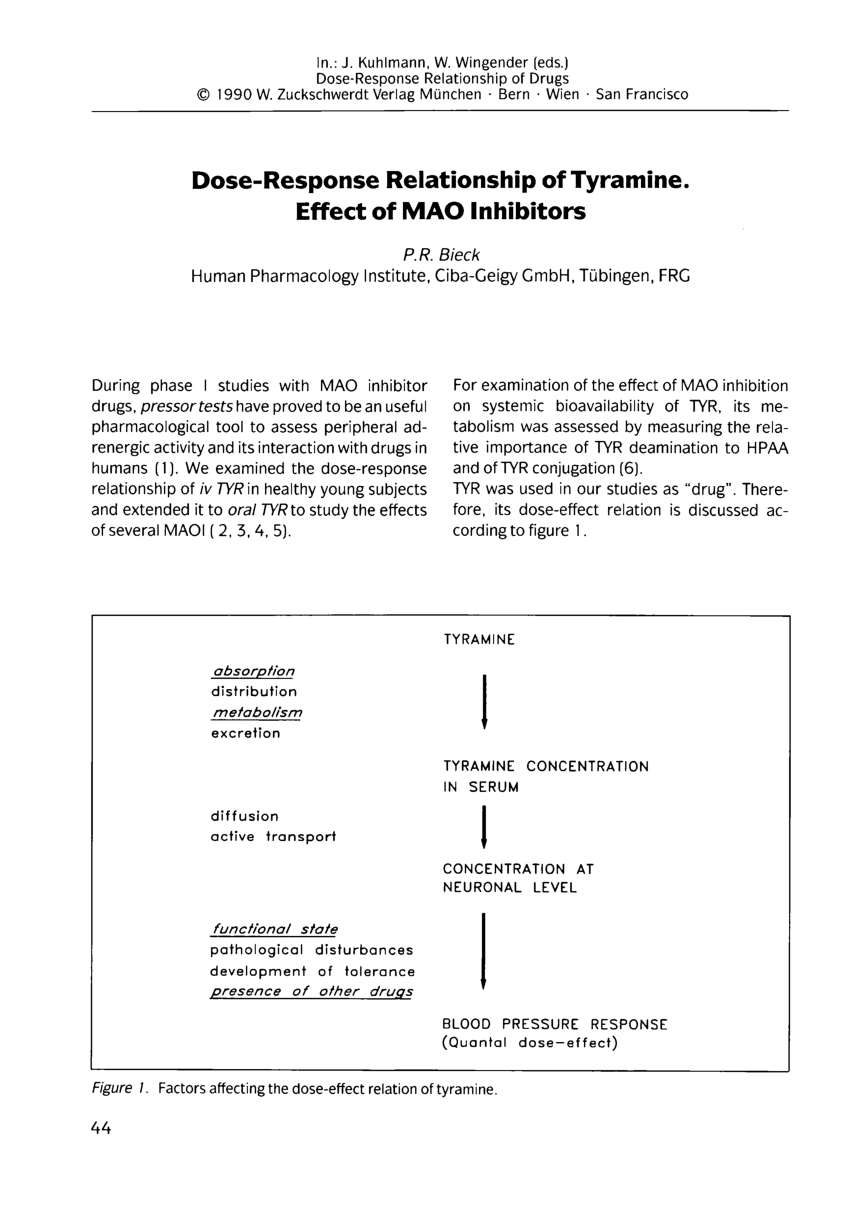


Pdf Dose Response Relationship Of Tyramine Effect Of Mao Inhibitors



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology
The fooddrug interaction between monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and high tyramine containing foods is one of the most dangerous combinations In today's post, I will discuss where you can find tyramine and the most common MAOIs out there that interact I will also discuss alternatives for foods containing tyramineHere are 6 potentially devastating fooddrug interactions that pharmacists should warn patients about 1 Chocolate, red wine, and antidepressants Along with many beers, aged cheeses, processed meats, and smoked fish, chocolate and red wine contain an amino acid derivative called tyramine Mixing tyramine with monoamine oxidase inhibitorsMAOIs (Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors)Instructional Tutorial VideoCanadaQBankcomVideo https//youtube/Cll4WVKJN30



Maoi Drugs News



Maois Diet Full Amino Acid Foods
But tyramine can reach dangerous levels if you eat foods containing tyramine while on an MAOI This can lead to a sudden spike in blood pressure, and to stroke, brain hemorrhage and death There have been nearly 100 deaths recorded due to interaction between pharmaceutical MAOIs and tyraminecontaining foodsReports of hypertensive reactions from monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) began to proliferate in the early 1960s Asatoor did extensive research and found that the combination of an MAOI and a food containing tyramine resulted in the hypertensive interaction ("the cheese reaction") Because of the risk of intracerebral hemorrhage and death,MAOA inhibition reduces the breakdown of primarily serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine;



8 Tyramine Free Ideas Migraine Diet Foods For Migraines Headache Diet






8 Tyramine Free Ideas Migraine Diet Foods For Migraines Headache Diet
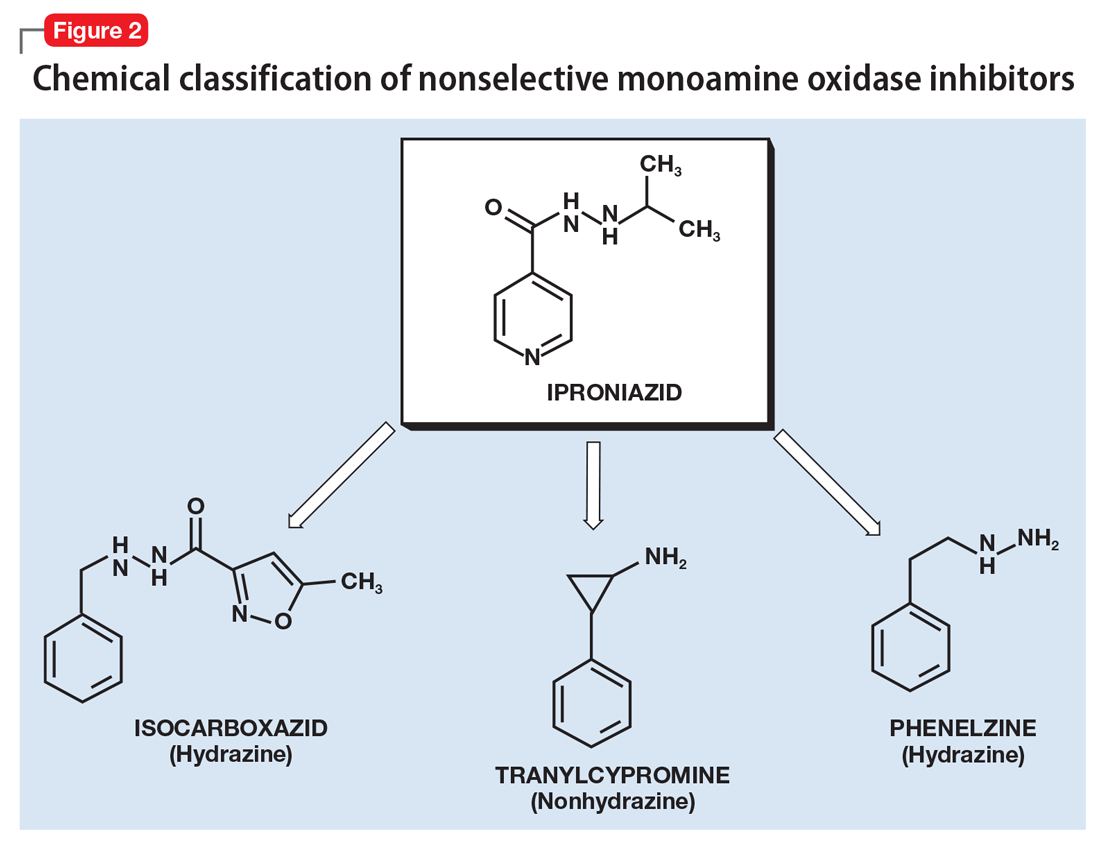


A Concise Guide To Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Mdedge Psychiatry


Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Wikipedia



Antidepressants Vaughan Asburys General Ophthalmology 17th Ed



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Osmosis
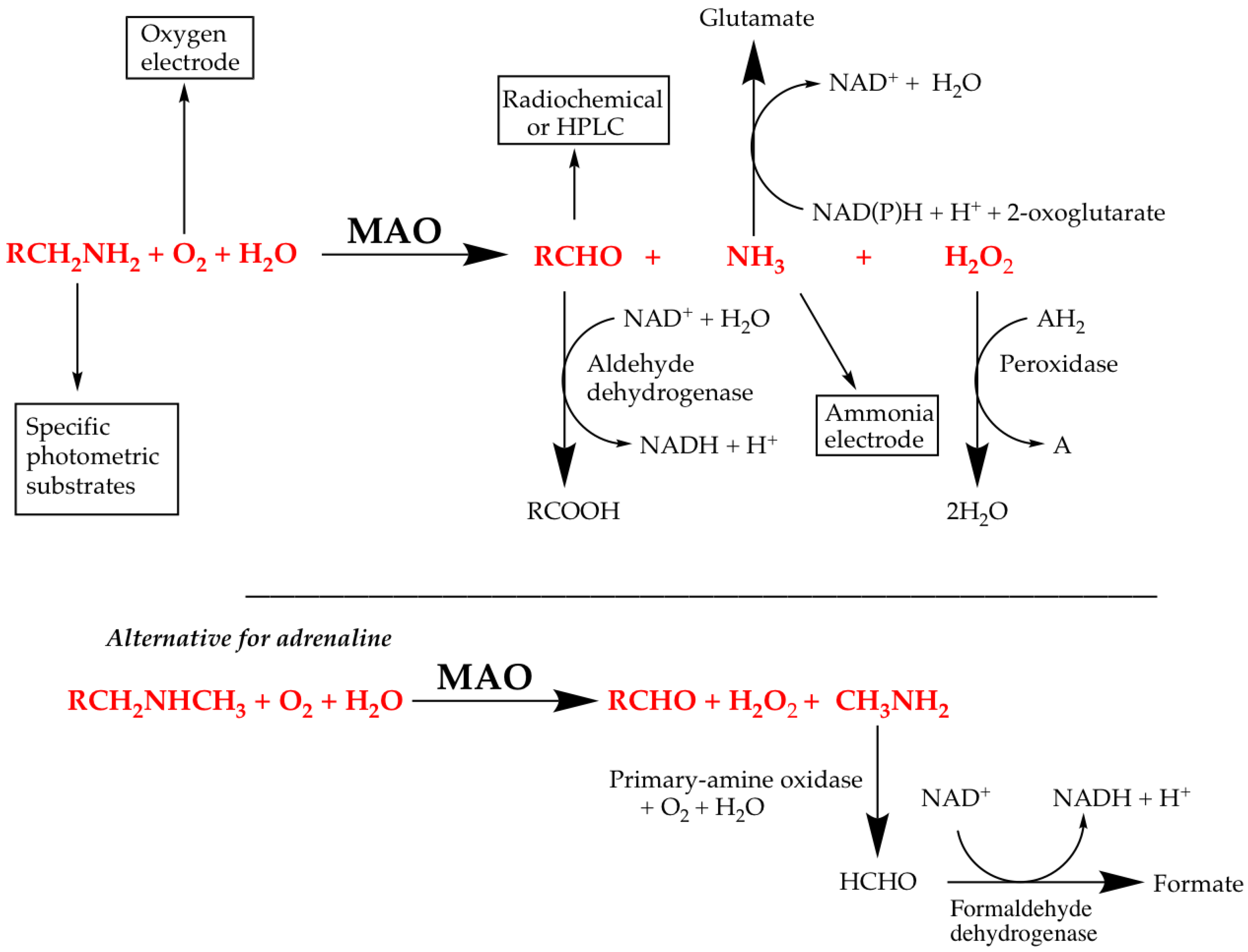


Molecules Free Full Text Assessment Of Enzyme Inhibition A Review With Examples From The Development Of Monoamine Oxidase And Cholinesterase Inhibitory Drugs Html



Antidepressants Ppt Download



Step Up Academy التيرامين Tyramine مادة توجد بشكل Facebook



Pdf Mao Inhibitors Risks Benefits And Lore Semantic Scholar



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry
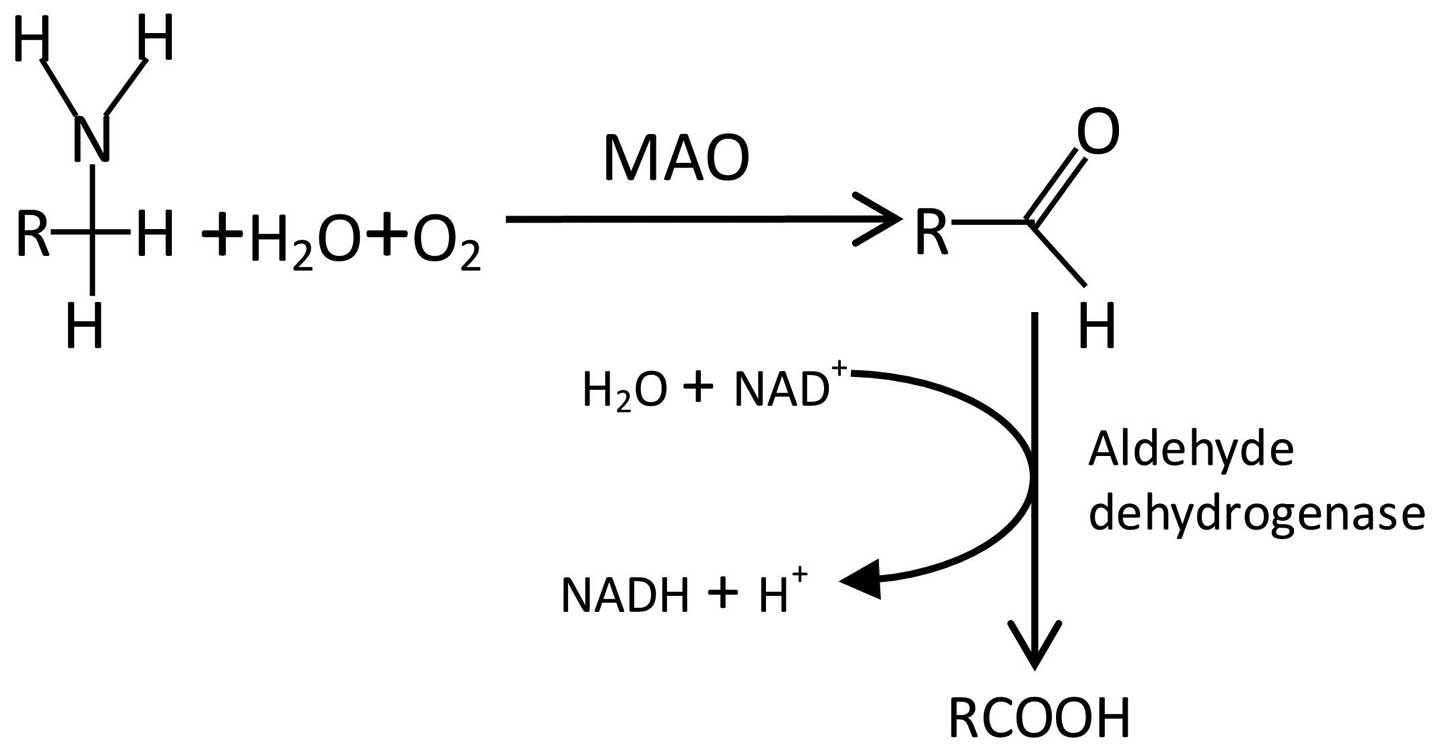


Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Promising Therapeutic Agents For Alzheimer S Disease Review



Influence Of Phenolic Compounds And Mao Inhibitors Or Ssao Inhibitors Download Scientific Diagram
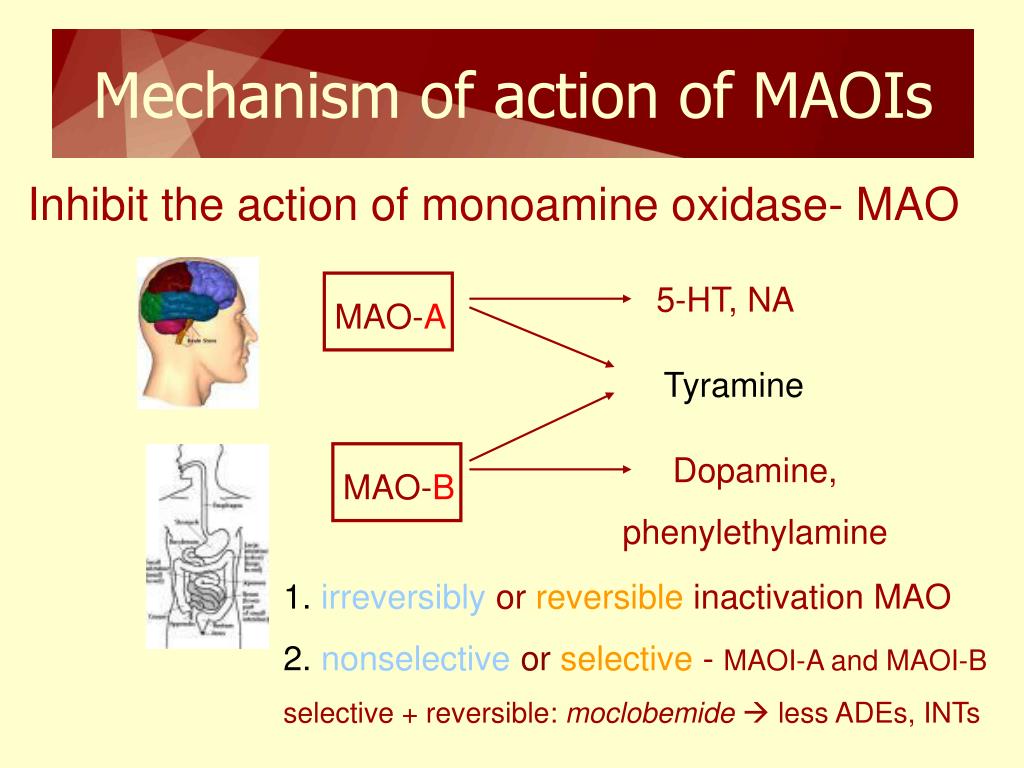


Ppt Pharmacology Section 10 Antidepressants And Mood Stabilizing Drugs Powerpoint Presentation Id



What Is Maoi Ssris Vs Maois For Treating Depression



Tyramine To Norepinephrine Maoi Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry



Antidepressants Amboss
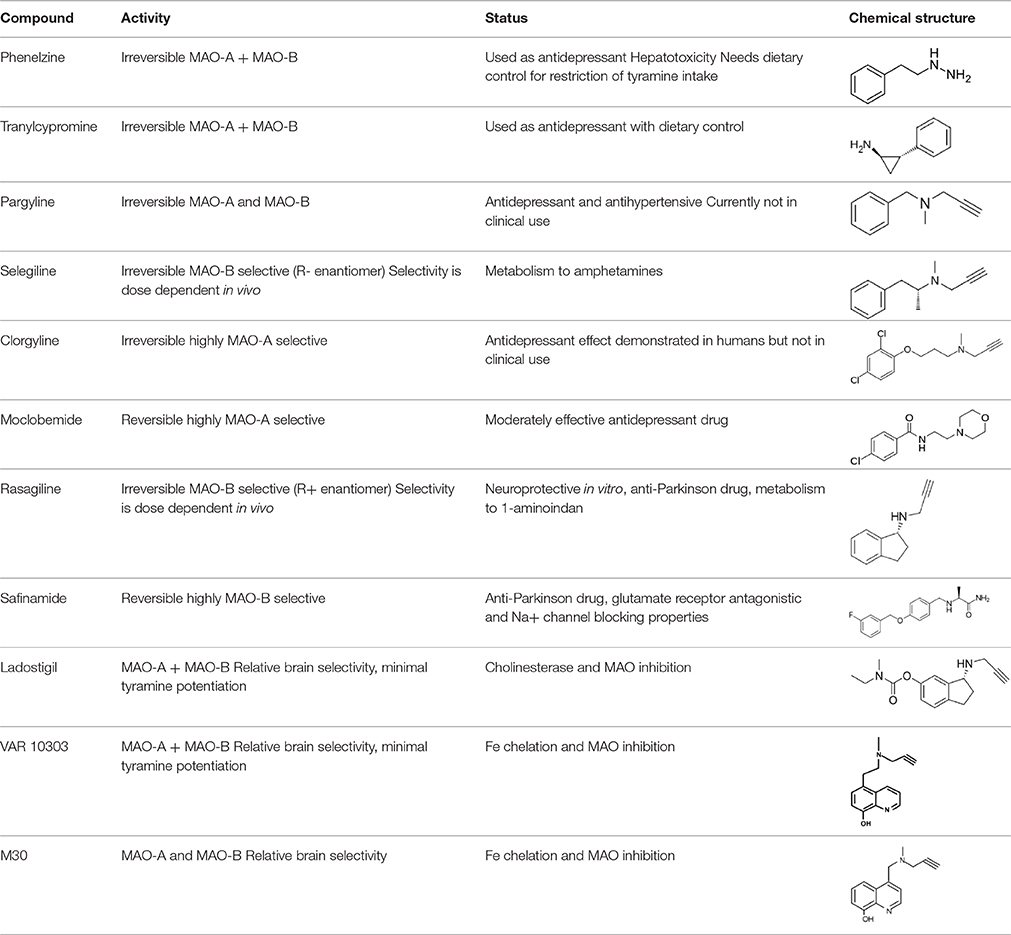


Frontiers Inhibitors Of Mao A And Mao B In Psychiatry And Neurology Pharmacology



Maoi Toxicity Litfl Toxicology Library Toxicants



What Are Mao Inhibitors Healthproadvice
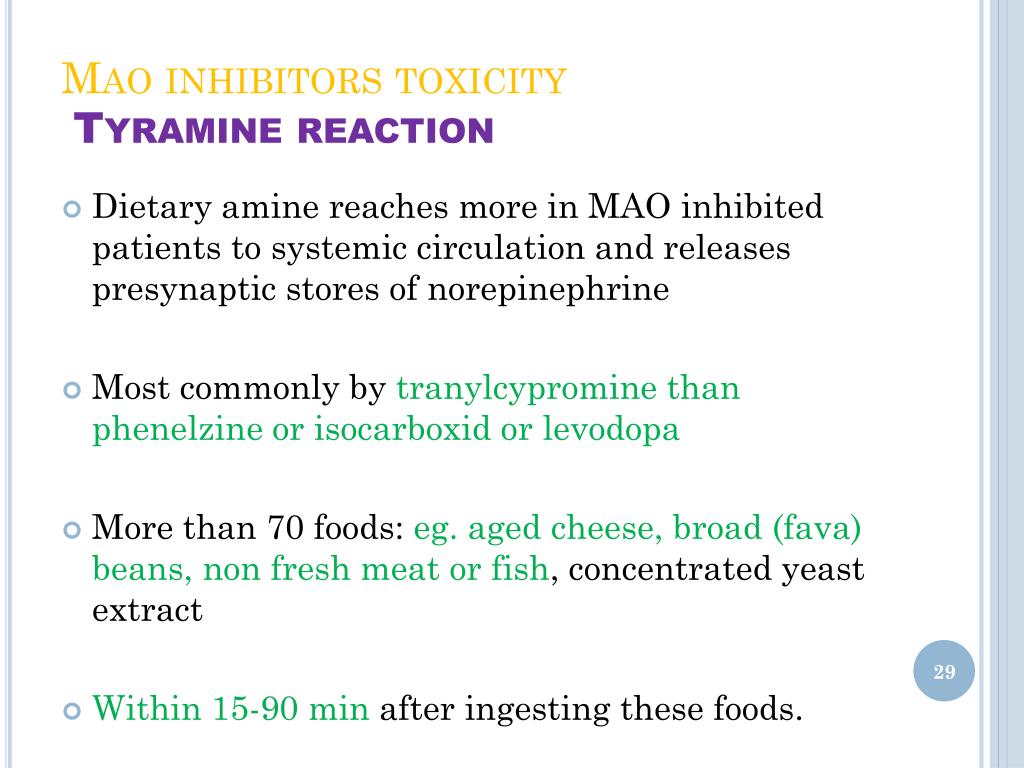


Ppt Management Of Specific Drug Poisoning Antidepressants Barbiturates Powerpoint Presentation Id



Slides Show



Curcumin And The Mao Inhibitor Cheese Effect From Induced Info



Drugs Summary Benzodiazepine Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor



Selegiline Wikipedia



Maoi Stimulant Hprs 2300 Acc Studocu



Many Soyfoods Suitable For Low Tyramine Diets Soy Nutrition Institute



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Chapter 1 Biogenic Amines Formation Toxicity Regulations In Food Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039



Slides Show



Meal Ideas And Menus Avoiding High Tyramine Foods Made Easy Kathrynne Holden Ms Rd Pdf Free Download



Mozzarella Maoi Diet Page 2 Line 17qq Com
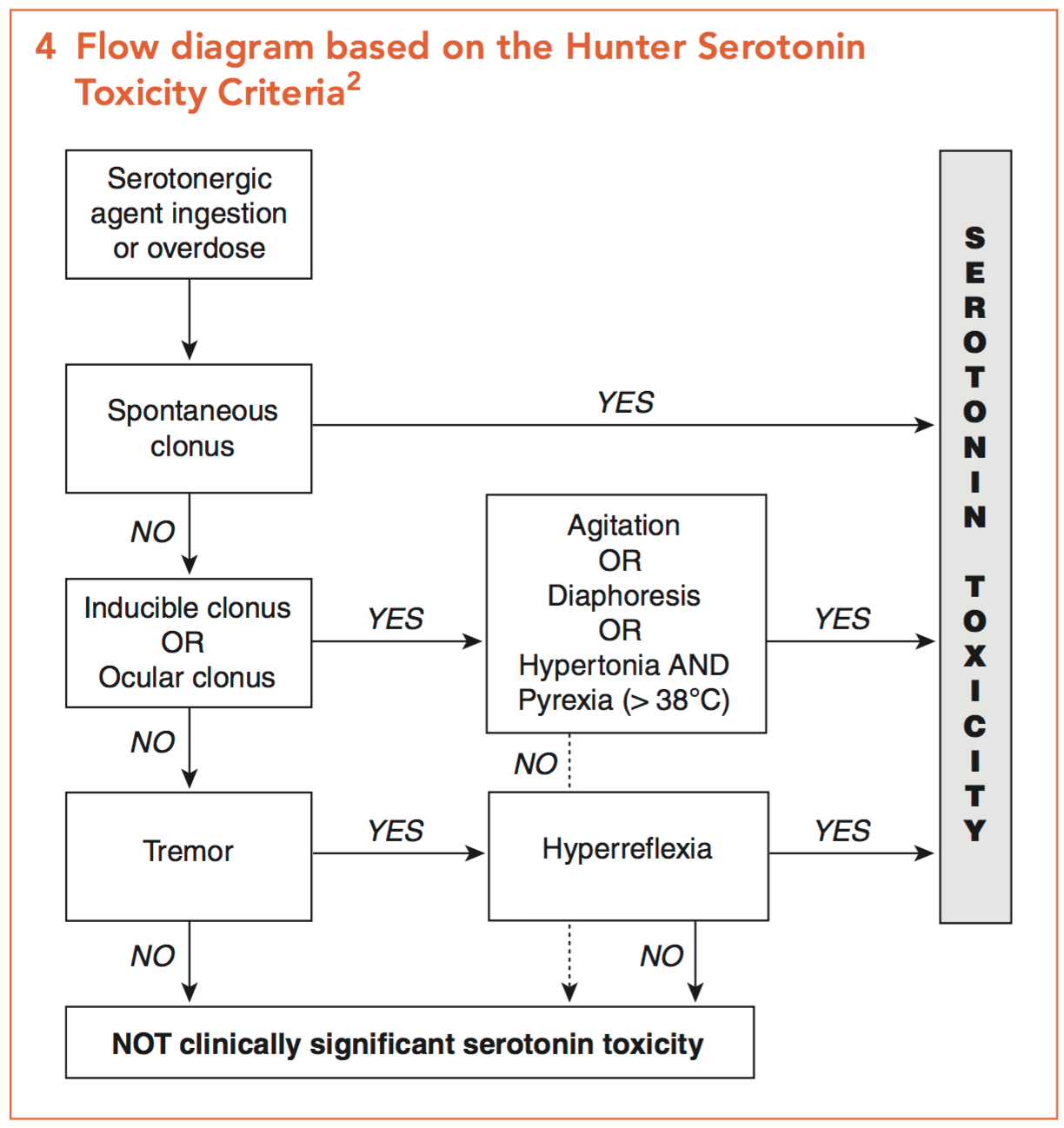


Maoi Toxicity Litfl Toxicology Library Toxicants



What Is Maoi What Are Mao B Inhibitors
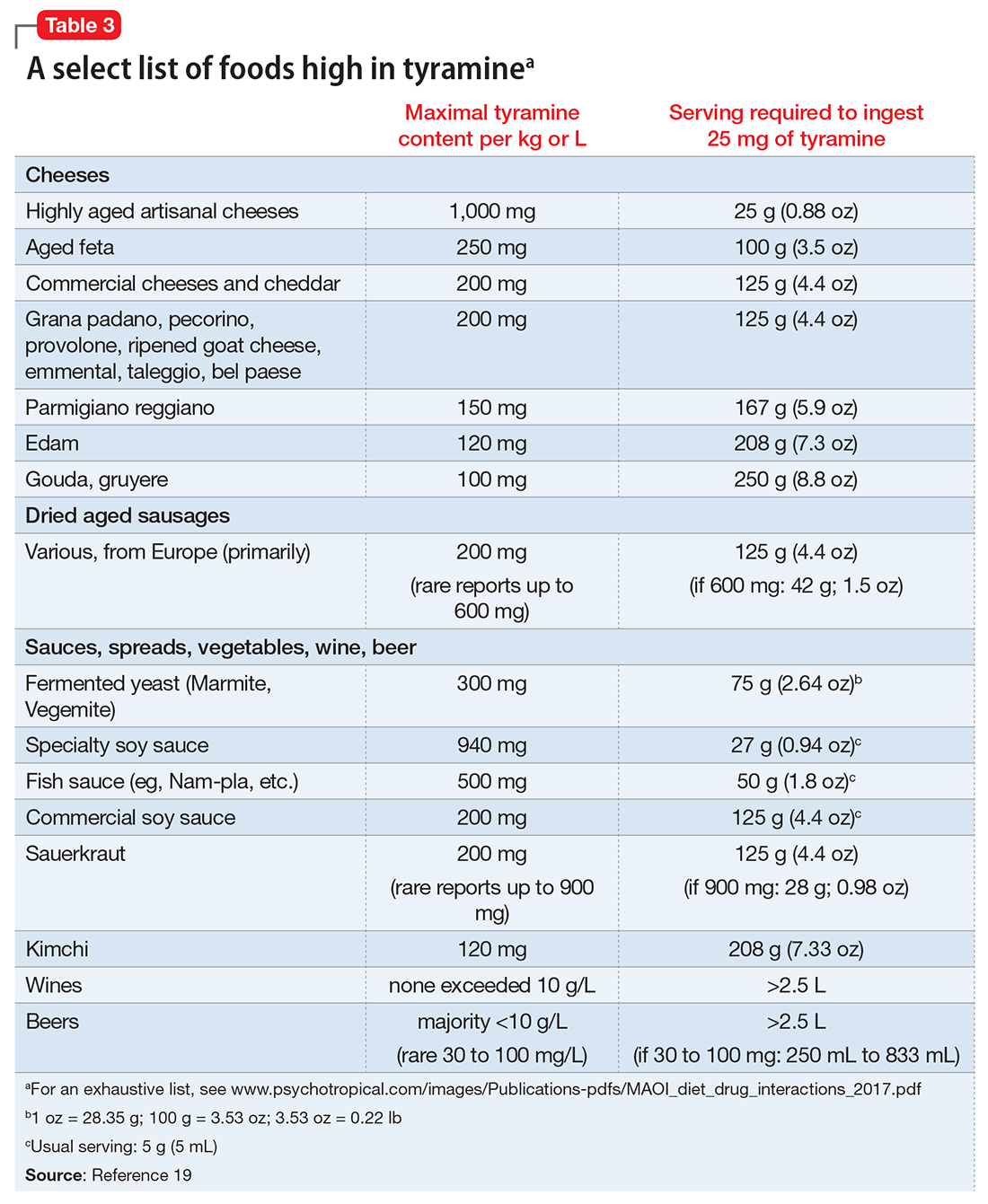


A Concise Guide To Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Mdedge Psychiatry



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maoi Mechanism Of Action Psychopharmacology



Antidepressants Vaughan Asburys General Ophthalmology 17th Ed
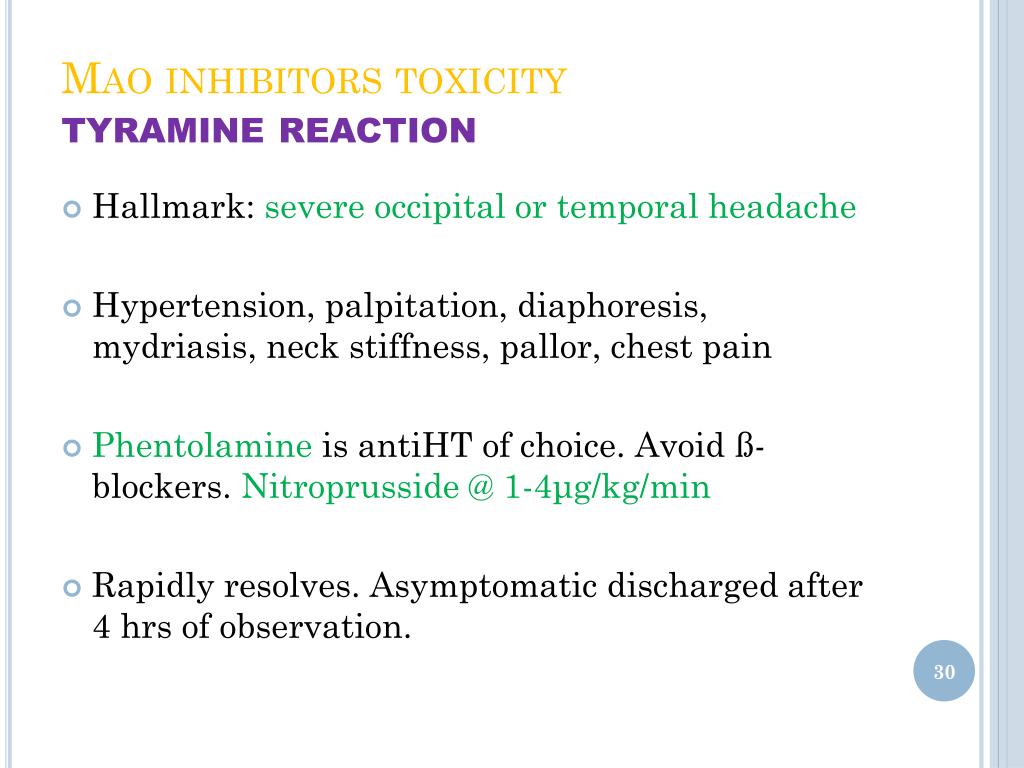


Ppt Management Of Specific Drug Poisoning Antidepressants Barbiturates Powerpoint Presentation Id



Awareness Of Interactions Has Come A Long Way Pharmacy Magazine



Sembragiline A Novel Selective Monoamine Oxidase Type B Inhibitor For The Treatment Of Alzheimer S Disease Journal Of Pharmacology And Experimental Therapeutics



Taar1 Dependent And Independent Actions Of Tyramine In Interaction With Glutamate Underlie Central Effects Of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibition Biological Psychiatry



What You Are Missing In Your Maois Notes Qd Nurses



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Maois
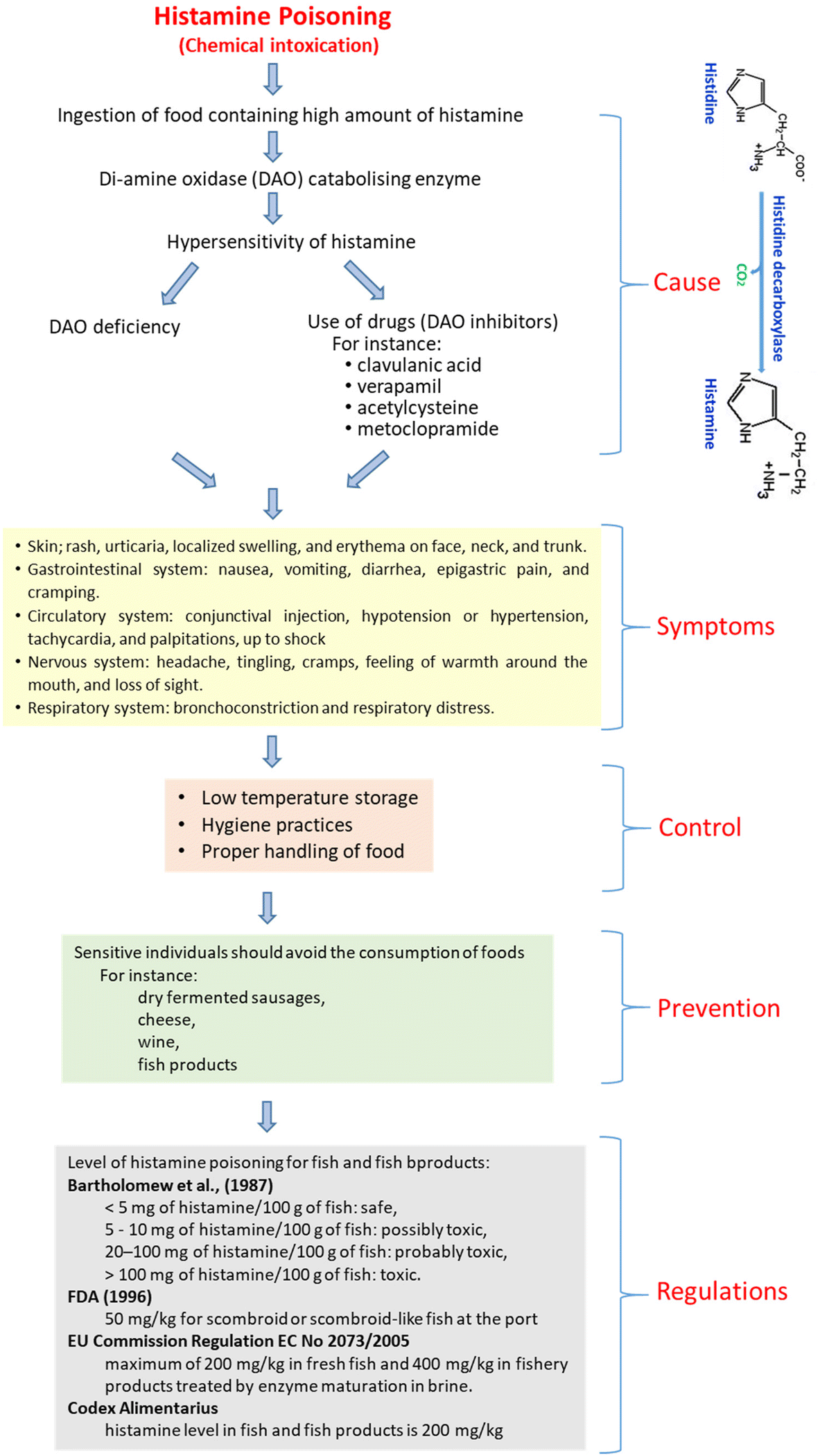


Chapter 1 Biogenic Amines Formation Toxicity Regulations In Food Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039



Antidepressants And Mood Stabilizers Ppt Download
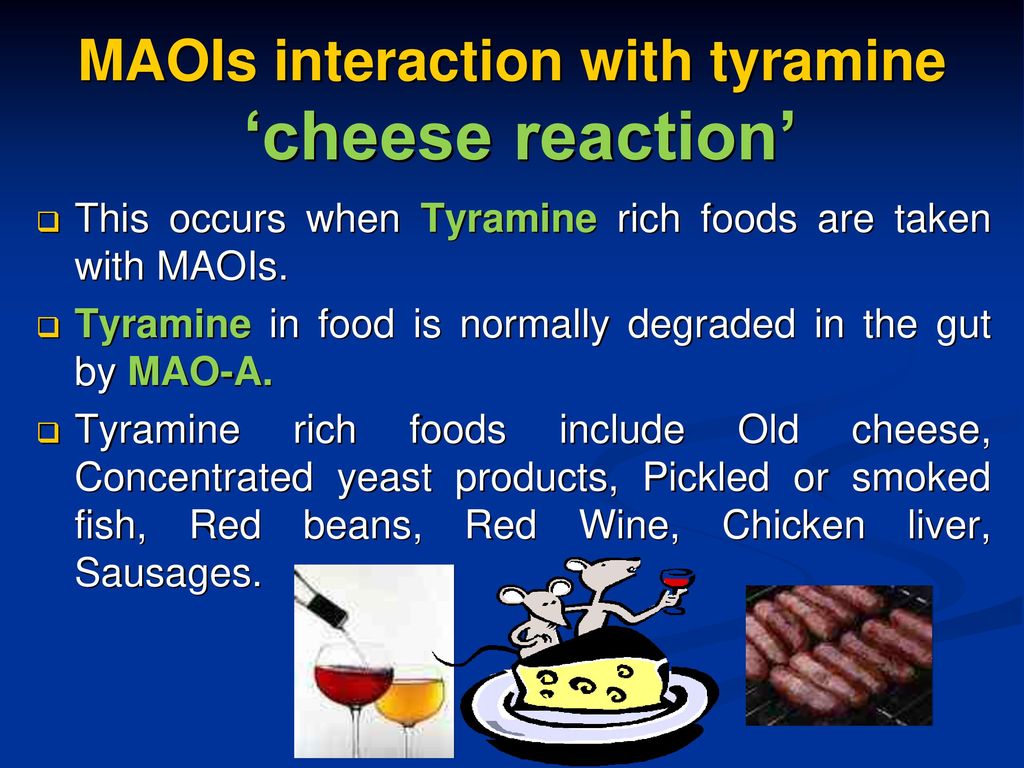


Drugs Used In Depression Prof Yieldez Bassiouni Ppt Download



Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Revisiting A Therapeutic Principle



Maois Diet High Tyramine Foods May Trigger Dangerous Side Effects



Food Drug Interactions Ppt Download
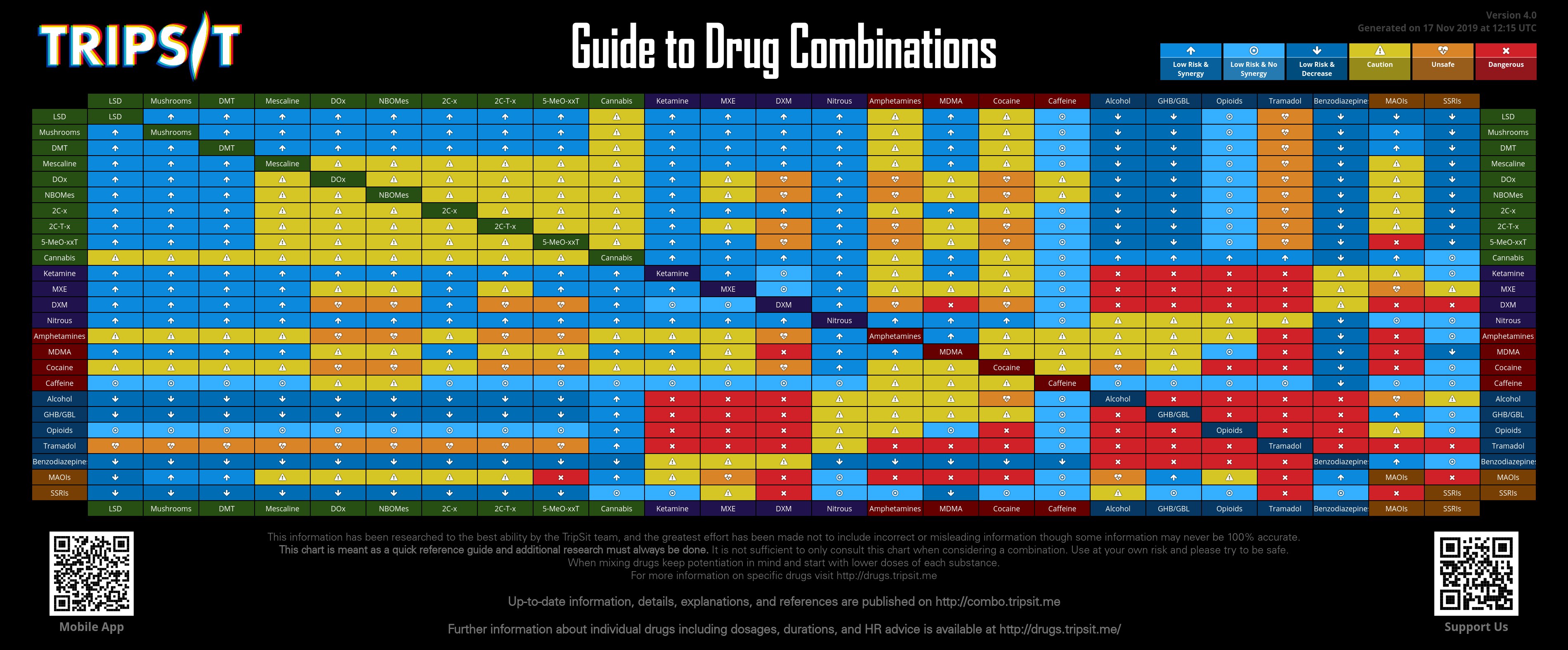


Drug Combinations Tripsit Wiki
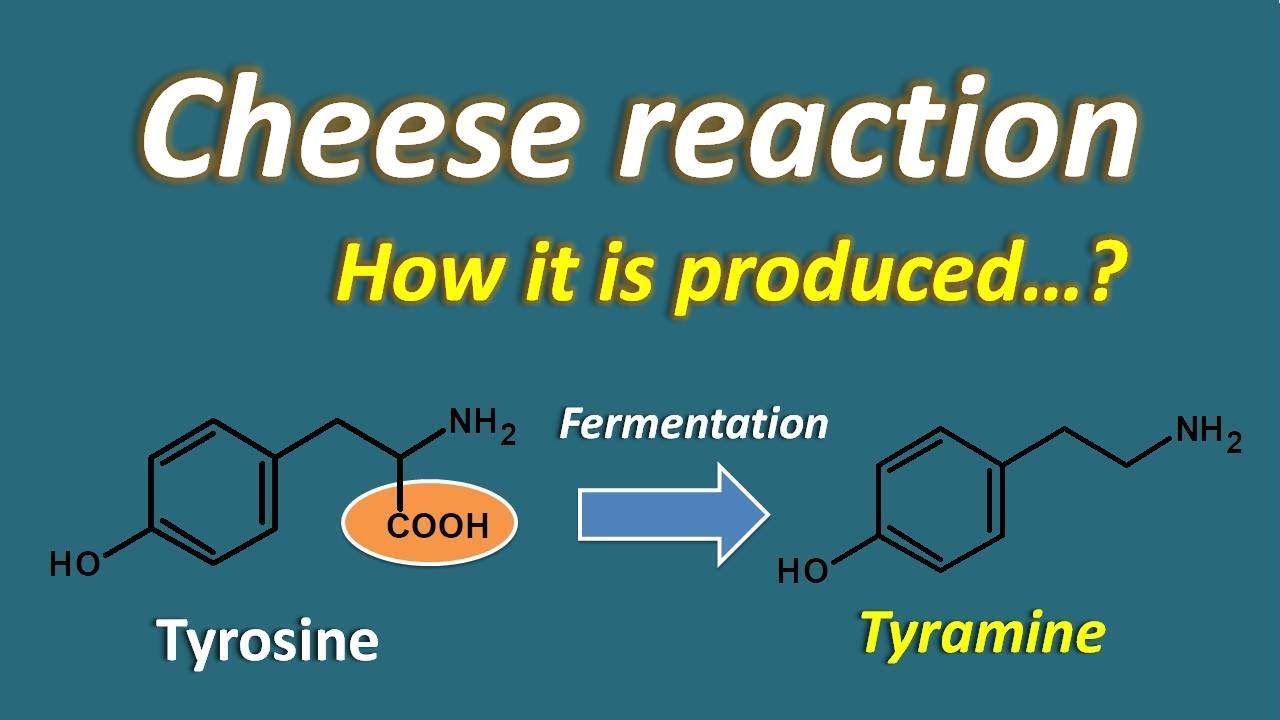


Cheese Reaction How It Is Produced Youtube


Maois Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Tyramine Toxicity Pharmacology Youtube
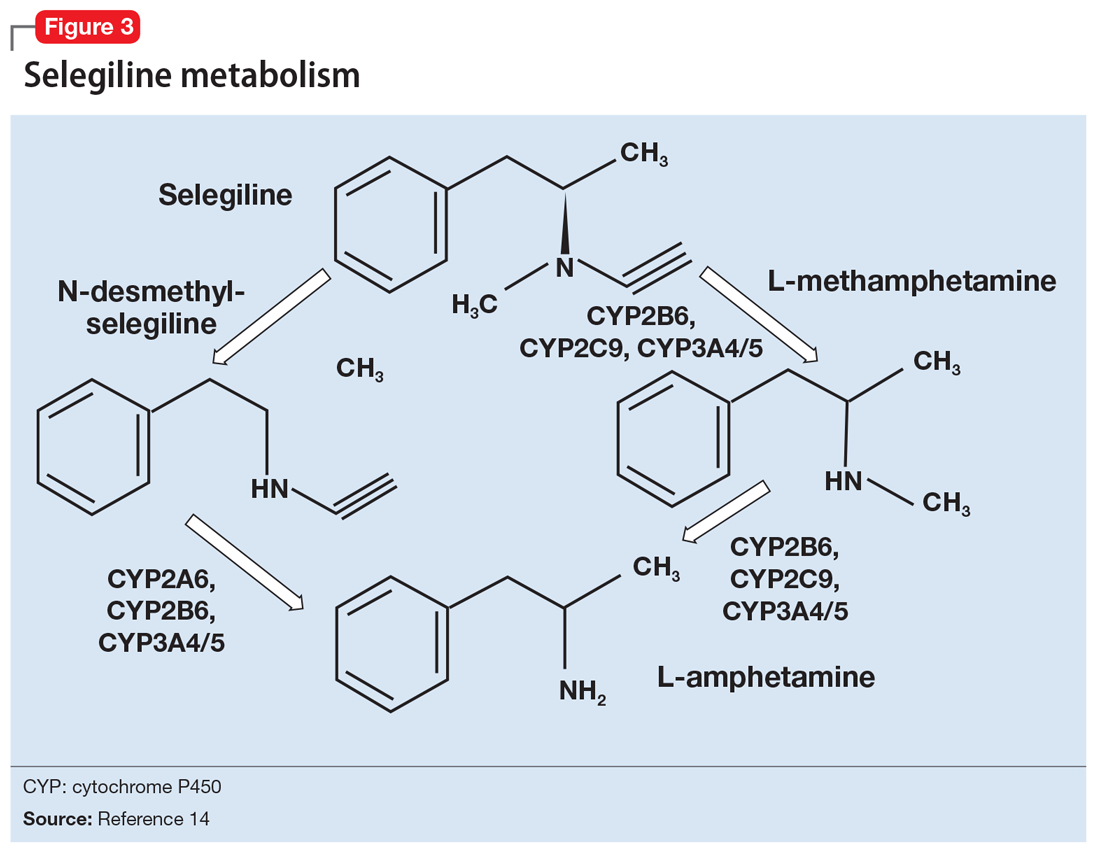


A Concise Guide To Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Mdedge Psychiatry



Body Fat Reduction Without Cardiovascular Changes In Mice After Oral Treatment With The Mao Inhibitor Phenelzine Carpene 18 British Journal Of Pharmacology Wiley Online Library



Pdf Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors Dietary Tyramine And Drug Interactions



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿